Pharmaceutical Gelatin

Gelatin capsules
Gelatin is widely used in the manufacture of hard and soft capsules, and has good biocompatibility and solubility which can protect the active pharmaceutical ingredients and improve bioavailability.
① Soft capsules
Gelatin has good film formation, flexiblity and biocompatibility, which can encapsulate drugs to form sealed capsules and effectively prevent the reaction of capsule shell and contents.
② Hard capsules
Gelatin is the main material of hollow capsules, and its high freezing strength makes it suitable for the manufacture of hollow hard capsules

Tablets
Gelatin can be used as a binder for tablets to help them form a solid structure and improve their temperature resistance and hardness

Hemostatic sponge
Gelatin sponges are widely used in surgery to control and terminate wound bleeding through their unique physical properties and biocompatibility
Plasma substitute
The advantages of gelatin as a plasma substitute are its good biocompatibility, low immunogenicity, and high cost performance
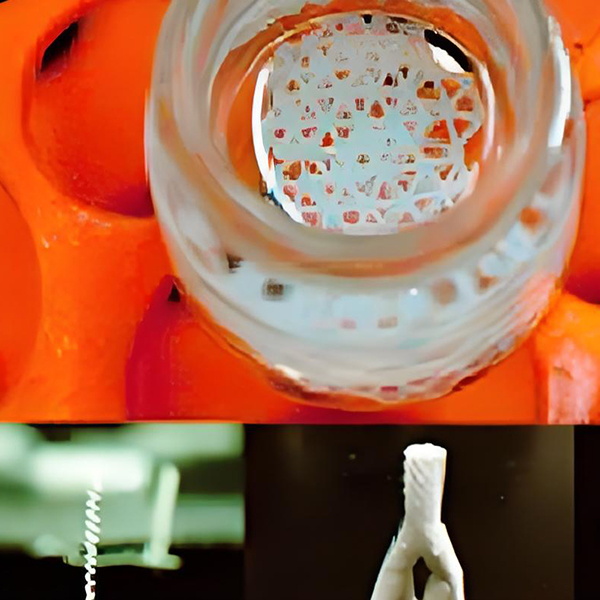

Tissue engineering stent material
As a scaffold material for tissue engineering, gelatin has excellent biocompatibility, degradability, cell adhesion, processability, and reversible sol-gel transition ability

